Talking to the Smartest Being Alive
(Who Knows Nothing About You)
Imagine you’re talking to the world’s smartest person who just woke up from a thousand-year nap. You ask them a question, and they immediately start answering but they have no idea who you are, what you know, or what language you even speak. That’s what it’s like when you talk to an AI with no context.
AI isn’t Google. You’re not throwing a question into the void and scrolling through a list of results, pretending you’ll check page two (we never do). Instead, you’re having a conversation with a system that’s trying to understand you. The better it knows your goal, your background, and even your style of thinking, the better it can tailor its answers.
We’re transitioning from solo investigation into true collaboration where research and discovery become a partnership between human curiosity and machine intelligence. This transition is more than mere convenience; it marks the beginning of closing the gap between searching, finding, collecting, translating, and understanding. We are in the age of removing the traditional barriers that once stood between knowledge and action.
- Accelerate Creativity: AI tools can help you brainstorm, iterate, and visualize ideas rapidly.
- Expand Your Toolkit: Access new styles, mediums, and workflows not possible before.
- Stay Relevant: Understanding AI keeps you competitive in a rapidly evolving art landscape.
AI is not a replacement for people, it's a powerful ally.
- A New Kind of Conversation
- Context - The Secret Ingredient
- The Language of Thought - LLMs
- Shaping the Output The Art of Balance
- Beyond Prompts - Enter the Agents
- The Mindset Shift - Teaching the Machine to Think With You
This process provides a high-level overview of what happens whenever AI is activated within a feature or application.
In Python, prompts are used to instruct AI models to perform targeted tasks by providing clear, detailed input. For example, you can write a prompt that asks an AI to summarize a document, generate code, answer questions, or extract information from text. The more specific and context-rich your prompt, the more accurate and useful the AI’s response will be. Experiment with different prompt styles-such as giving examples, specifying the output format, or breaking tasks into steps-to see how the model’s output changes for your use case.
1. A New Kind of Conversation
Picture this: you open your laptop and type your first message to AI. You ask it something simple “How can I learn coding fast?” You wait for the answer like it’s Google, expecting a list of tutorials and videos.
But AI doesn’t search it thinks. It gathers everything it knows, blends it together, and tailors an answer for you. The only problem? It doesn’t know who you are yet. That’s why your job, before anything else, is to set the stage.
When you start a new chat, tell it about yourself: your skill level, what you want to achieve, even how you like information delivered. That’s how AI stops guessing and starts collaborating.
Example:Think of AI like meeting a genius traveler who knows everything about the world’s history but has never heard of your hometown. Before you can ask meaningful questions, you need to give them your map.
2. Context – The Secret Ingredient
AI prompting isn’t about magic words; it’s about context. Think of it like meeting a new teammate. The first thing you do is introduce yourself.
The better you frame the situation, the smarter your results. For example:
- “I’m a beginner with no coding experience.”
- “I learn best from examples and analogies.”
- “Explain new terms simply as if you’re teaching a friend.”
Context tells AI how to think with you, not at you. It turns information into understanding and transforms random output into something built exactly for your brain.
Example:Asking an AI “Write a marketing strategy” with no details is like asking a chef to “make dinner.” If you add, “for a small bakery launching an online store on a tight budget,” you’ll get recipes that actually make sense.
3. The Language of Thought - LLMs
Behind the scenes, large language models (LLMs) act like translators for human thought. They take our messy ideas and shape them into structured reasoning, code, summaries, and creative concepts.
You’re not coding in some abstract machine language anymore you’re coding in your language. Every time you write a prompt, you’re teaching an analytical partner how to think like you.
Example:Google is like a library index it points you to books. AI is like a friendly librarian who listens, thinks, and writes a summary tailored to what you actually need.
4. Shaping the Output The Art of Balance
You’ve probably noticed AI sometimes gets too creative or too stiff. That’s because of the “temperature knob.”
- A low temperature (0.2) keeps answers focused and logical.
- A high temperature (1.0) encourages imagination and diverse ideas.
Experiment with it like seasoning food: find the right mix of precision and creativity for your task. And there are other ingredients too: top-p, top-k, frequency and presence penalties each shaping how your AI writes, reasons, and repeats.
Example:A low temperature makes AI write like a lawyer, formal and precise. A high one makes it sound like a storyteller or artist. It’s the difference between reading a report and hearing a campfire story.
5. Beyond Prompts Enter the Agents
Now, imagine promoting your AI from assistant to operator. Enter AI agents. These are self-directed digital teammates that can plan, reason, execute tasks, and even call other tools on your behalf.
They remember past instructions, use APIs, and adjust strategies in real time.
Their workflow looks like this:
- Understand the objective.
- Plan the approach.
- Execute and analyze.
- Improve through feedback.
To manage them, a Super Admin ensures everything is safe, secure, and organized keeping your expanding AI team aligned with your goals.
Picture this: you tell your AI agent, “Research local competitors, draft a summary, and email me the findings.” The agent does it, no copy-pasting required. It’s like having an employee who never gets tired or distracted.
6. The Mindset Shift - Teaching the Machine to Think With You
This isn’t just a tech lesson; it’s a new relationship with information itself.
We’re not searching anymore, we’re teaching.
We feed AI data, context, goals, and in return, it helps us think, build, and create.
AI isn’t replacing understanding; it’s amplifying it. The better we feed and guide it, the smarter and more human-aligned it becomes. That’s the future not just using AI, but growing with it.
Example:Think of AI like training a loyal dog or mentoring a new teammate. The more you communicate, the more it learns your style and anticipates what you need. Over time, it stops following commands and starts collaborating.
7. Prompt Library
Click any prompt box to instantly copy expert prompts for AI collaboration. Organized into 8 categories from context setting and goal clarification to agent style operators and meta-prompts this library transforms vague AI chats into productive partnerships, perfect for presentations or daily use.1. Introduce yourself (context prompts)
I'm [role] with [experience level] in [domain]. My goal is [goal]. I prefer explanations that are [style: e.g., visual, step-by-step, or analogy-driven]. Before answering, ask up to three clarifying questions about my context.
Assume you just woke up after 1,000 years and know nothing about me. Ask me the most important 5 questions to understand my background, my project, and how to best help me.
Act as a collaborative partner, not just a question-answer machine. Start by summarizing your understanding of who I am and what I'm trying to achieve, then propose how you can help.
2. Clarify the goal (task framing)
Help me define my goal more clearly. Ask questions, then rewrite my goal as: 'From [current state] to [desired outcome] by [timeframe], measured by [success metric].'
I'm not sure exactly what I need. Based on this rough idea: [paste idea], suggest 3 possible concrete tasks we could work on together and recommend one to start with.
Before solving anything, restate the problem in your own words, list assumptions you are making about my goal, and ask me to confirm or correct them.
3. Teach the AI your style
Here is how I like information: [bullets: e.g., short, structured, with examples, minimal jargon]. When you answer, follow that style and tell me if my request is missing anything critical.
Act like a [tone: e.g., coach / tutor / consultant / engineer / storyteller]. Use that voice while keeping the content accurate and practical.
Explain this to me as if I'm [beginner / intermediate / expert] in [topic]. If I seem confused, automatically slow down and add simpler examples.
4. Turn vague asks into good prompts
You can show "bad vs better" using these:
- Role you should play: [role]
- My background: [summary]
- Goal & constraints: [goal, time, tools]
- Output format: [bullets, table, code, checklist]
- Level & tone: [beginner/expert, formal/casual]
5. AI as collaborator (not a search box)
Don't just answer; propose a plan. First, give a 3-step plan for how we should tackle this together. Then execute step 1 and ask for my feedback before continuing.
Treat this as an ongoing collaboration. At each step, tell me: what you're doing, why, and what you need from me to improve the result.
When I give you a draft (idea, email, code, slide), respond with:
A quick diagnosis of strengths and weaknesses,
3 concrete improvement suggestions,
An improved version,
One question to help refine further.
6. Control creativity (temperature-style prompts)
These let you talk about "temperature knobs" in human terms:
Give me a low-creativity answer: precise, cautious, and focused on reliability, like a careful lawyer.
Now give me a high-creativity version: exploratory, full of fresh angles and metaphors, like a storyteller. Keep facts accurate.
For each idea, label it as: Safe & Conventional / Balanced / Bold & Unusual so I can choose how creative to go.
7. Agents / operator-style prompts
To connect with the "promote your AI from assistant to operator" idea, use:
You are my AI operator. For this request, you should:
Plan the steps,
Ask any missing questions,
Execute as much as possible on your own,
Present a summary plus next-step suggestions for me.
Act as an autonomous research assistant. Task: [research goal]. You should search, synthesize, and produce:
A short executive summary,
Key findings,
Risks or gaps,
Questions you still have for me.
Behave like a project manager AI. Given this objective: [objective], create a mini-roadmap, assign yourself subtasks, and walk me through progress step by step.
8. Meta-prompts to improve prompts
These are great to end the library and show "we're not searching, we're teaching":
Critique my last prompt. Rewrite it to be clearer, more contextual, and more actionable for you, and explain what you changed and why.
From our conversation so far, create a 'profile prompt' that describes who I am, how I think, and how you should work with me. I'll reuse it at the start of future chats.
Suggest 5 reusable prompts I can save in a personal library for: learning, writing, decision-making, brainstorming, and planning, tailored to my background.
1. AI App Process
This process provides a high-level overview of what happens whenever AI is activated within a feature or application.
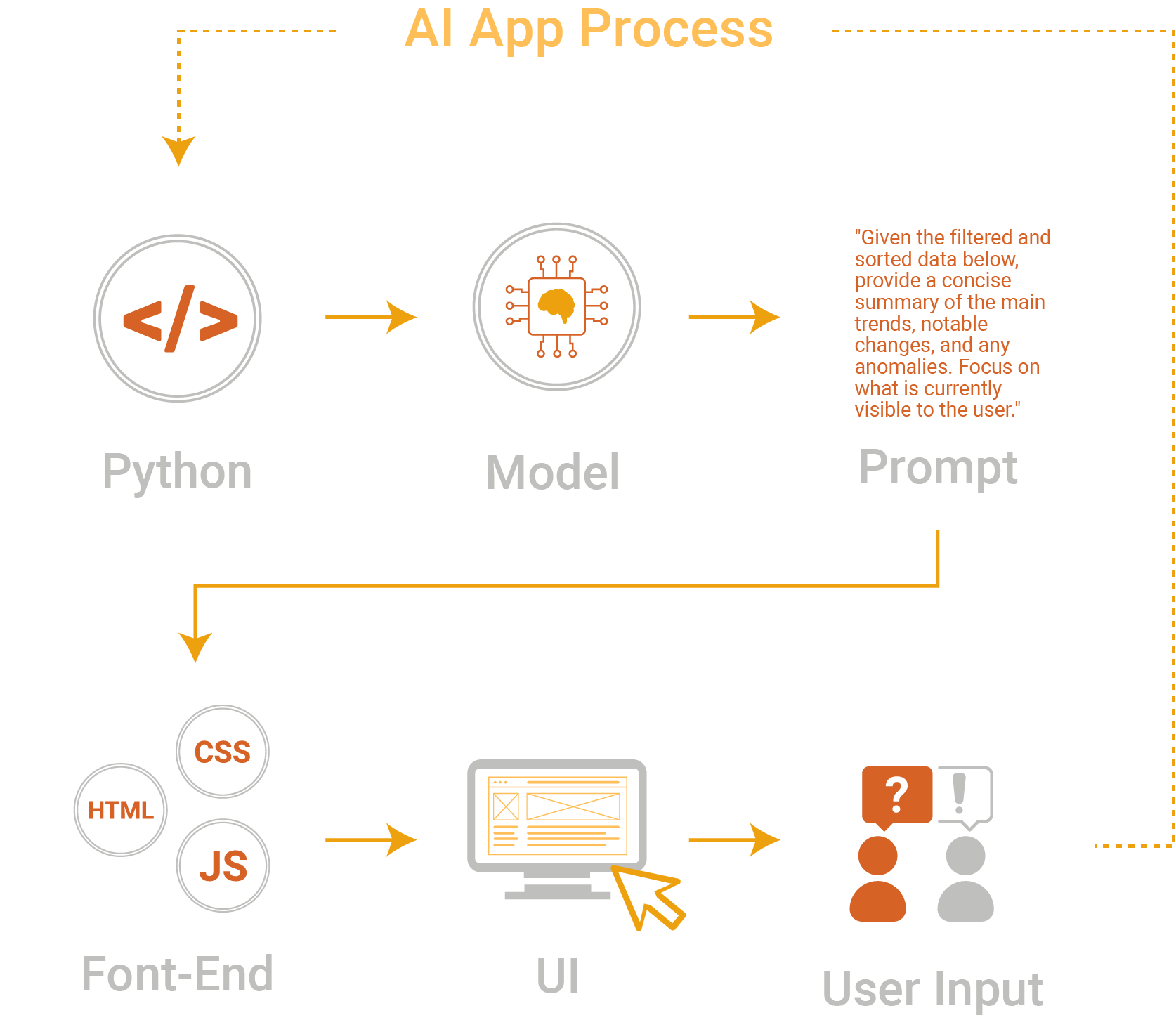
2. Summarize My Data Table
A user activates the feature: "Summarize My Data Table" A panel that provides instant, AI-generated summaries of the currently visible data.
3. Using Python Code
The most widely used coding language for AI apps is Python due to its simple syntax, extensive libraries (like TensorFlow, PyTorch, and scikit-learn), and strong community support.

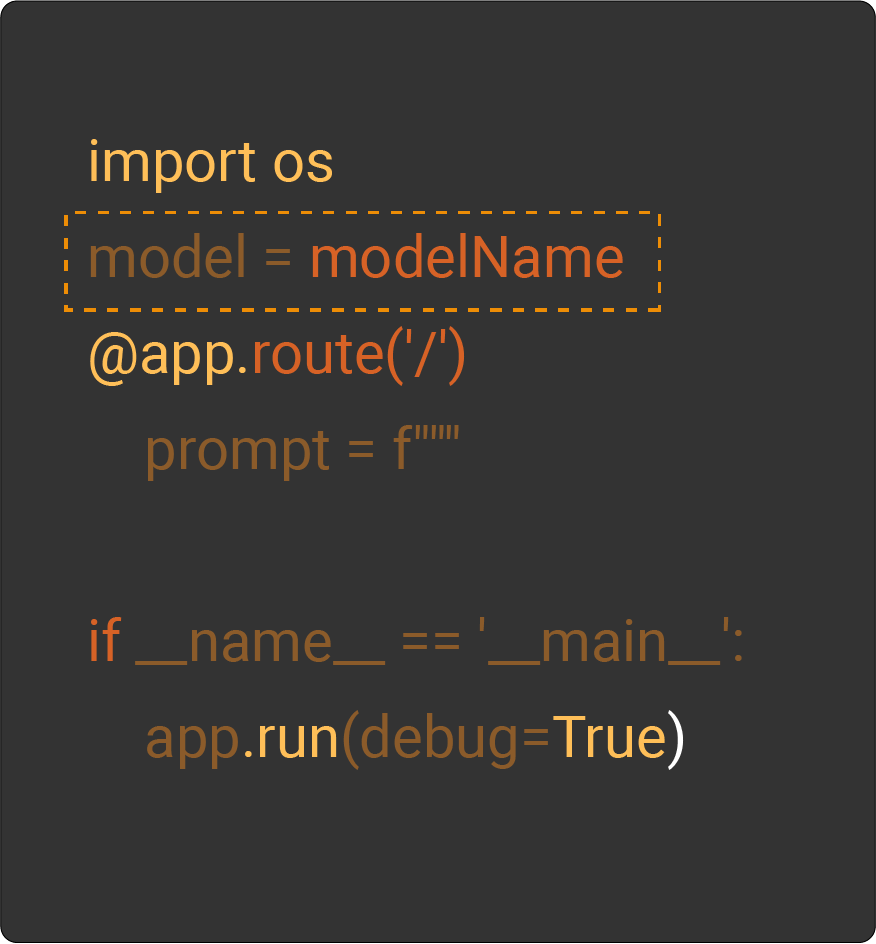
4. API's Models, & Credentials
The first trigger is imported libraries or API clients then a specified model you want to use along with your authentication credentials.
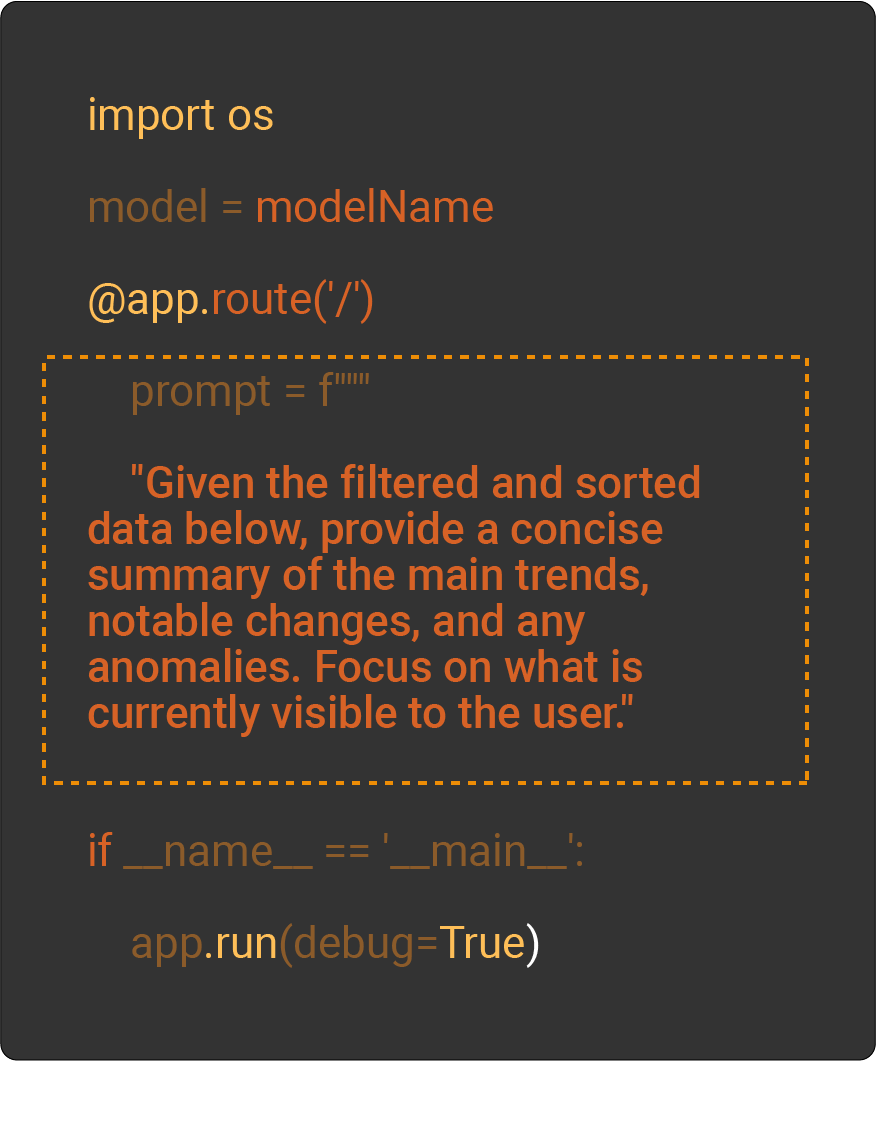
5. In code Prompt-text
Next, prompt-text inputs or instructions-to the model through function calls, and the model returns generated responses. This integration lets your Python app interact seamlessly with the AI, enabling it to process prompts and deliver intelligent outputs in real time.
6. Front-End Builds
Basic Layout of HTML, CSS, and JavaScript is utilized to communicate and render a front-end interface visual for the end user.
- HTML: Structures the content.
- CSS (styles.css): Styles and positions the elements.
- JavaScript (script.js): Adds interactivity.
